Root Cause Analysis / Problem-Solving training course is based on the Eight Disciplines (8D) approach to structured problem-solving. Having a disciplined methodology creates a foundation for learning, measuring problem-solving progress, and helping to manage expectations during crisis situations, large or small. This training course will spend time on root cause analysis using some common quality tools and techniques.
- Understand the importance of performing root cause analysis.
- Identify the root cause of a problem using the problem-solving process.
- Understand the application of basic quality tools in the problem-solving process.
- Compare results from a structured problem-solving approach versus past practice.
- Streamline your problem-solving process while improving relationships with your internal and external customers.
- Learn a standardized approach that you can apply across an entire organization for fixing problems permanently.
Team-Based Problem Solving
- Addresses Complicated Problems:
The team approach works best when the problem as well as its associated information, is complicated and beyond what one member is reasonably capable of knowing.
- Addresses Special Cause and Common Cause Problems:
The 8-D process was designed to work best with special cause problems. However, it can also be associated with common cause problems and improvement actions like those associated with a QOS.
- Uses Cross-functional Inputs:
Working in a cross-functional team means that each problem solver no longer needs to know all the technical details about how things work. Necessary information is available from a variety of team members.
- Promotes Standardization:
A team approach to problem-solving leads to a common language. This promotes effectiveness, consistency, time savings, and change control.
- Designed for Problems with Unknown Root Causes:
The problem-solving process is used to identify the root causes of problems and provide corrective action.
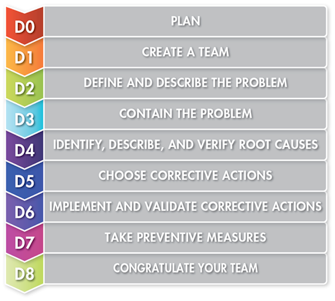
The 8-D Problem Solving Process
The Eight Disciplines (8-D) comprise a method of resolving a problem when the cause of the problem is unknown.
- Encompasses the Entire Process:
As a Problem-Solving Process, it is a sequence of events that should be followed from the moment a problem or improvement opportunity is evident.
- Facilitates Timely Solutions
When correctly followed, it helps to facilitate a timely resolution to the problem.
- Provides a Reporting Format
- The 8-D Report is a living document.
- Progress to date
- An action plan for completion.
- The 8-D Report is used to communicate progress on resolving a problem. It may serve as a reference for future efforts.
- Establishes a Standard Practice
- An emphasis on facts, where problem-solving, decision making, planning are driven and monitored by hard factual data.
- A commitment to solving the origin of the problem, not just masking the effects of the problem.
- An enforced discipline.
Team Problem Solving Objectives
Establish a small group of people with the process/product knowledge, allocated time, authority, and skill in the required technical disciplines to solve the problem and implement corrective actions. The group must have a designated champion.
Specify the internal/external customer problem by identifying in quantifiable terms the who, what, when, where, why, how, how many(5W2H) for the problem.
- Implement and Verify Interim (Containment) Actions:
Define and implement containment actions to isolate the effect of a problem from any internal/external customer until corrective action is implemented. Verify the effectiveness of the containment action.
- Find and Verify Root Causes:
Identify all potential causes which would explain why the problem occurred. Isolate and verify the root cause by testing each potential cause against the problem description and test data. Identify alternative corrective actions to eliminate the root cause.
- Select Permanent Corrective Actions:
Though test programs quantitatively confirm that the selected corrective actions will resolve the problem for the customer, and will not cause undesirable side effects. Define contingency actions, if necessary, based on risk assessment.
- Implement Permanent Corrective Actions:
Define and implement the best permanent corrective actions. Choose on-going controls to ensure that the root cause is eliminated. Once in effect, monitor the long term impact and implement contingency actions, if necessary.
Modify the management systems, operating systems, practices, and procedures to prevent recurrence of these and any other similar problems.
Recognize the collective efforts of the team and learn from what they did.
A hat is assigned to each step in the process:
Blue hat – What is the issue? What is the scope of the discussion?
White hat – What do we know for sure? What data is available to us? Only review the facts during this phase.
Red hat – What do we feel? What is our gut feeling? Focus on emotions in this phase.
Green hat – What ideas do we have? What could we do? Creativity only in this phase, there should be no criticism or cynicism and anything goes, the more outlandish the ideas the better.
Yellow hat – What benefits might some of these ideas bring? What advantages do they have? Be optimistic and positive in this phase.
Black hat – What concerns do we have over the ideas expressed? How practical are they? What expense might be involved? Don’t be afraid to challenge ideas.
Blue hat – The team should return to the blue hat and ask: where are we in addressing the issue? Has the scope widened? Do we have a solution or a path to a solution?
Think positively!
Motivating your team is vital when things appear to go wrong in a process. Appreciative coaching consists of gathering the team together and spending an hour simply talking about what is going well to accentuate the positive. Taking time out to appreciate the strengths of the people in the team, the software, the hardware, all aspects of the process can be very motivational and might just lead to opportunities to make improvements.
Ask ‘why?’
One of the most common reasons for mistakes is human error but does that make us lazy and is that always the root cause? The Five Whys technique finds the root cause of a defect by encouraging the team to answer the question ‘why?’ five times, leading to the deeper cause of the problem.
Problem-Solving Training in Jordan
If you are looking for Problem-Solving Training in Jordan, you are at the right place! AAC MENA is one of the best providers to obtain the Problem-Solving Training for your industry in Jordan at an affordable price. AAC MENA is known for ensuring customer satisfaction and business improvement.
Conclusion
As a leader in consultation services, AAC MENA offers unrivaled experience and expertise in Problem-Solving Training. Our presence in the Middle East and harmonized approach give you access to the largest independent network of consultants and advisory services in the region.
To discuss our Problem-Solving Training, contact us today.